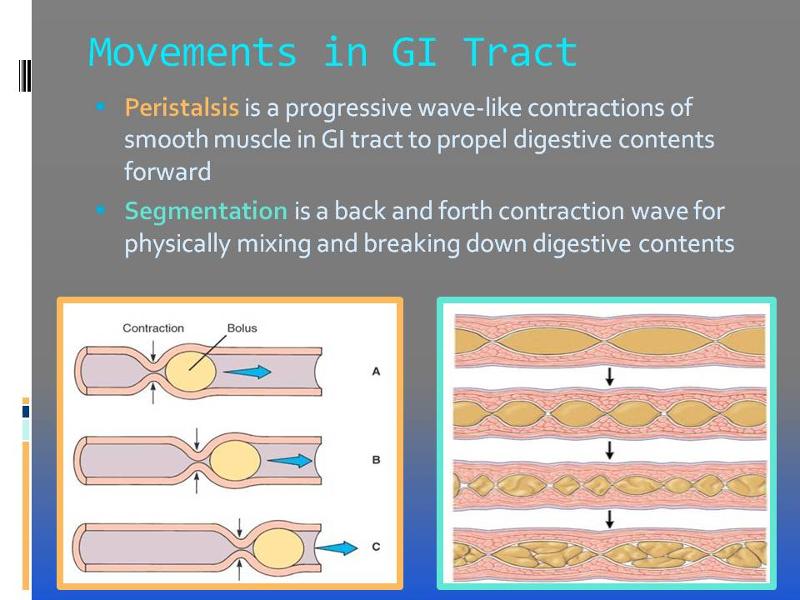
Video/Image Link Peristalsis
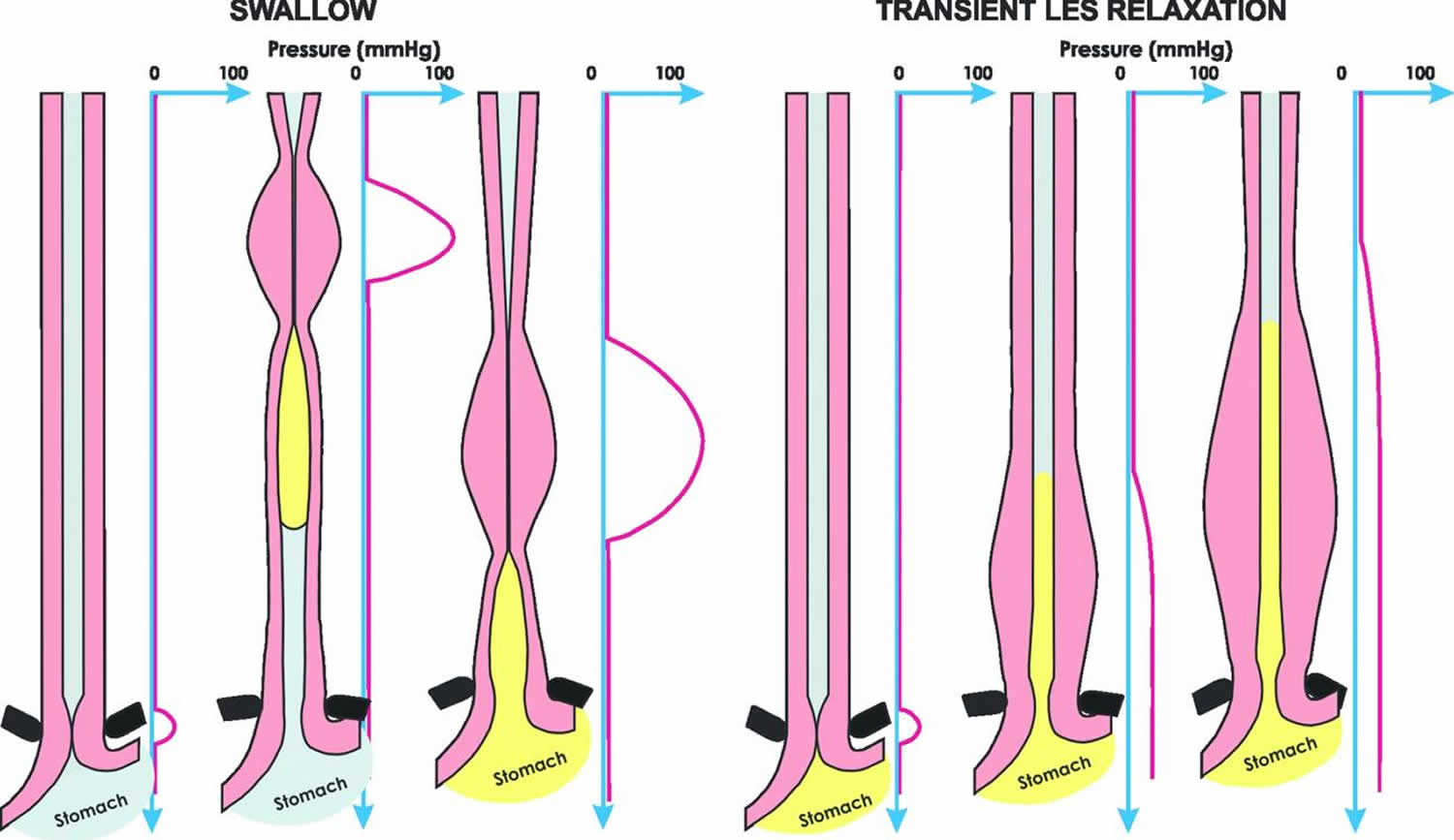
Peristalsis consists of sequential, alternating waves of contraction and relaxation of alimentary wall smooth muscles, which act to propel food along (Figure 1). These waves also play a role in mixing food with digestive juices. Peristalsis is so powerful that foods and liquids you swallow enter your stomach even if you are standing on your head.

Peristalsis and segmentation Diagram Quizlet
Q. Offer a theory to explain why segmentation occurs and peristalsis slows in the small intestine. A. The majority of digestion and absorption occurs in the small intestine. By slowing the transit of chyme, segmentation and a reduced rate of peristalsis allow time for these processes to occur. Q. It has been several hours since you last ate.
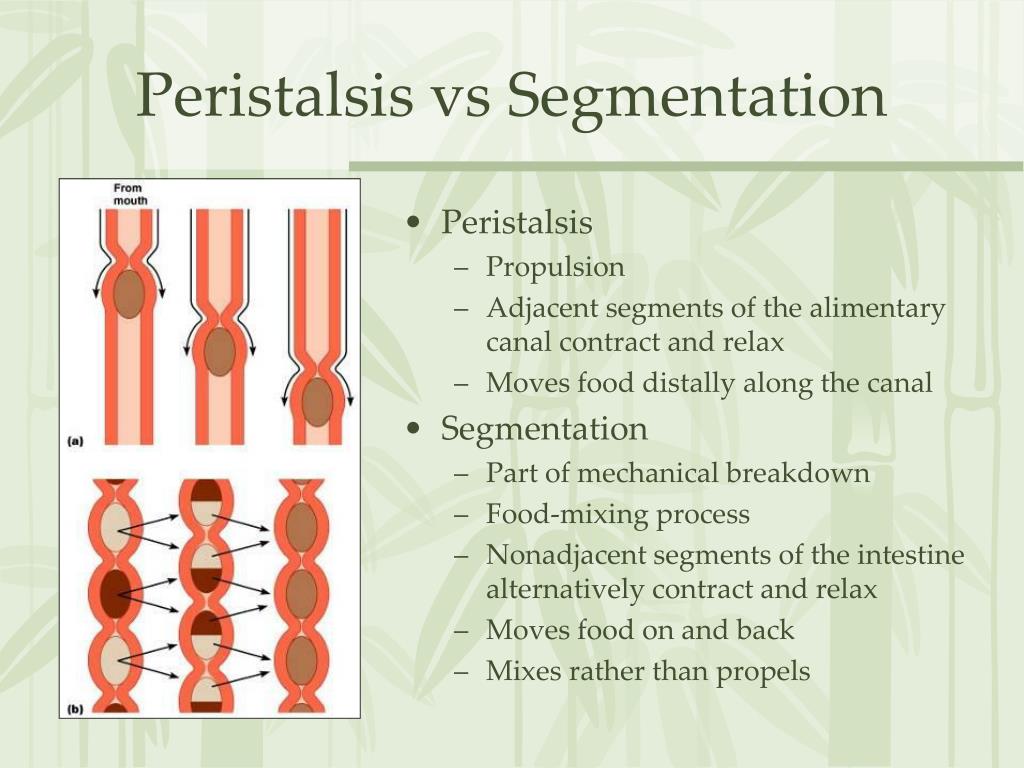
PPT The Abdomen PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5535939
The peristaltic movement, also known as peristalsis, is the contraction and relaxation of the oesophagus and the food pipe, which causes the food to be pushed down the track to the stomach. This involuntary movement is required to transport food through the stomach and bowels through the anus.
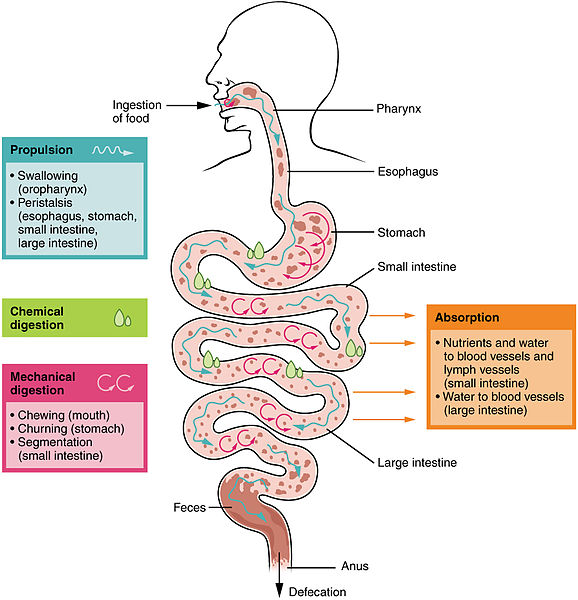
What is the Difference Between Peristalsis and Segmentation
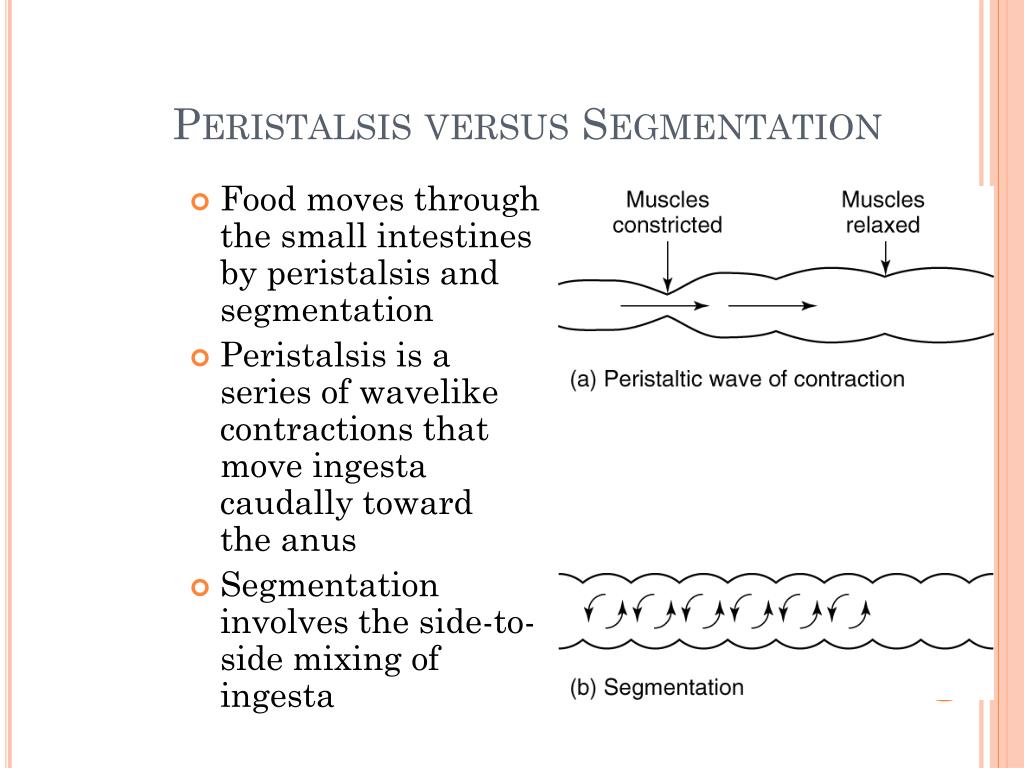
Segmentation and peristalsis: Segmentation, Peristalsis, Mechanical digestion, Small intestine, Absorption, Digestive system, Nutrients, Anatomy & Physiology.

Peristalsis Definition, Functions, Disorders, Examples and FAQs
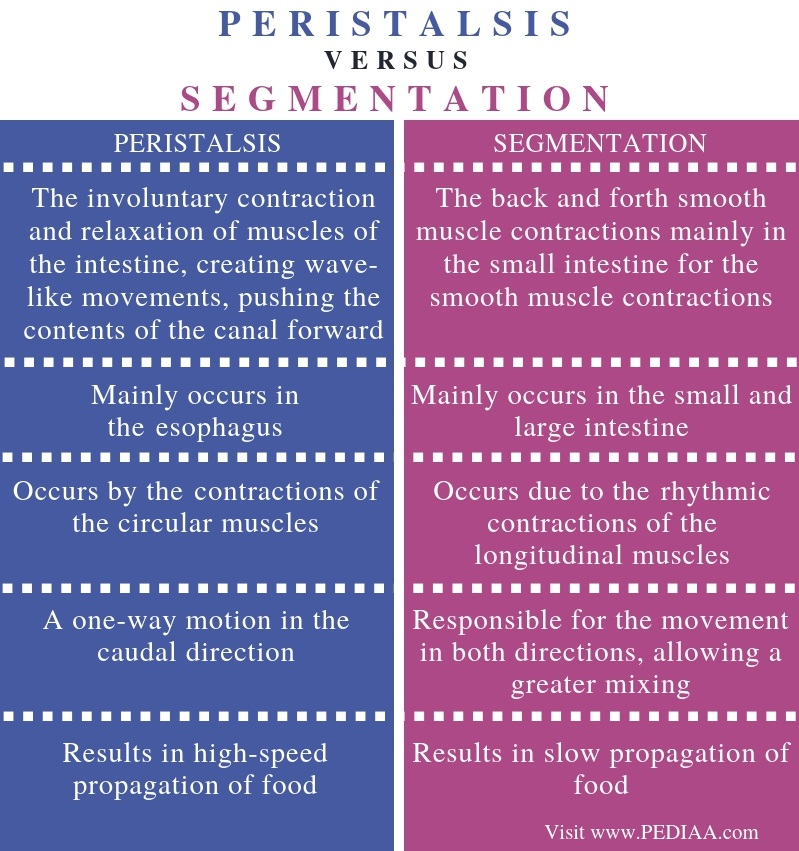
Peristalsis and segmentation are two types of muscular movements that occur in the gastrointestinal tract. They are responsible for the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract. Key Areas Covered 1. What is Peristalsis - Definition, Characteristics, Importance 2. What is Segmentation - Definition, Characteristics, Importance 3.
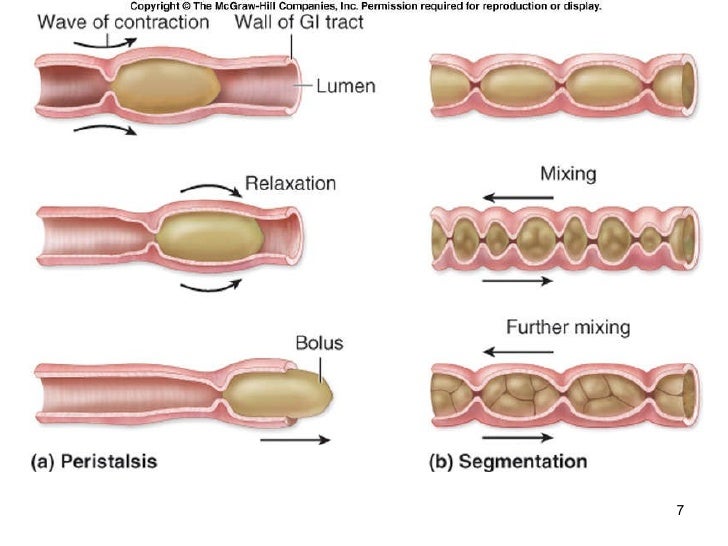
Chapter 26, f 09
Peristalsis consists of sequential, alternating waves of contraction and relaxation of alimentary wall smooth muscles, which act to propel food along ( Figure 23.5 ). These waves also play a role in mixing food with digestive juices.

Movement Through the Small Intestine Peristalsis, Segmentation & Pendular Movement YouTube
Digestion and Absorption

Anatomy & Physiology Peristalsis in the Small Intestine ditki medical & biological sciences
1 Definition. Peristalsis, segmentation, haustration and mass movement are contraction of the intestinal muscles that mix and propel intestinal contents in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The gastrointestinal tract is made up of the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine that are separated by sphincters.

Review Peristalsis and Segmentation in the Small Intestine ditki gastrointestinaltract
Q. Offer a theory to explain why segmentation occurs and peristalsis slows in the small intestine. Answer. A. The majority of digestion and absorption occurs in the small intestine. By slowing the transit of chyme, segmentation and a reduced rate of peristalsis allow time for these processes to occur. Q.
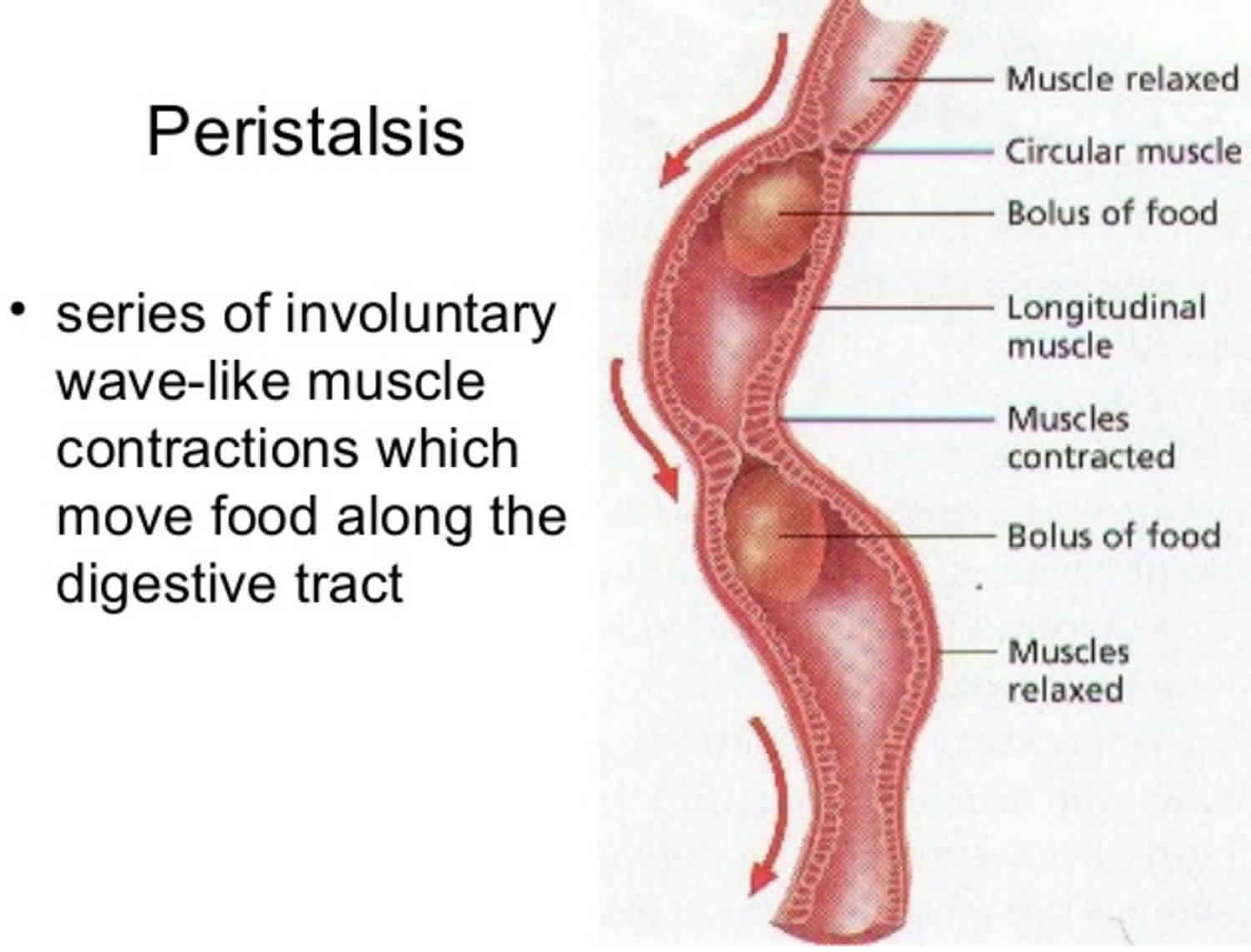
Peristalsis function, where peristalsis occurs & peristalsis in the digestive tract
Peristalsis is the involuntary contraction and relaxation of longitudinal and circular muscles throughout the digestive tract, allowing for the propulsion of contents beginning in the pharynx and ending in the anus.
What is the Difference Between Peristalsis and Segmentation
Peristalsis moves food through the digestive tract with alternating waves of muscle contraction and relaxation.. Offer a theory to explain why segmentation occurs and peristalsis slows in the small intestine. It has been several hours since you last ate. Walking past a bakery, you catch a whiff of freshly baked bread..
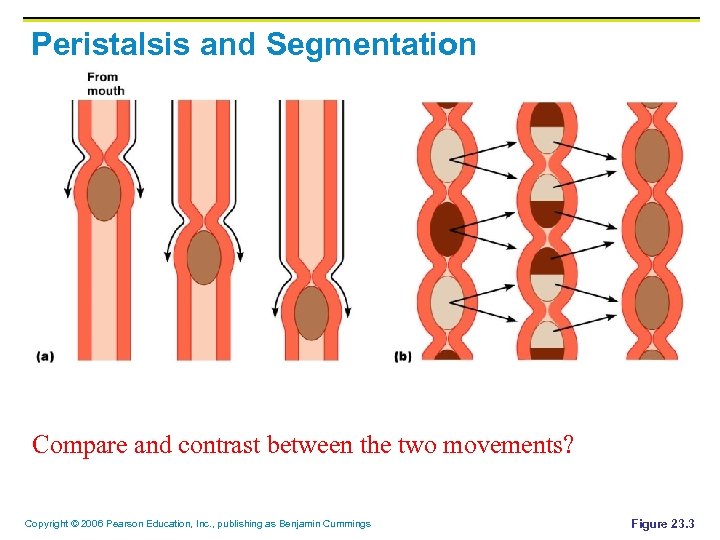
Chapter 23 The Digestive System Copyright 2006
Effective peristalsis requires an active myenteric plexus. Depression or complete blockade of peristalsis can be seen in the congenital absence of the myenteric plexus, termed Hirschsprung disease, or by utilizing atropine to paralyze the cholinergic nerve endings of the myenteric plexus.

Digestion Peristalsis vs Segmentation Renal physiology, Anatomy and physiology, Digestive
peristalsis, involuntary movements of the longitudinal and circular muscles, primarily in the digestive tract but occasionally in other hollow tubes of the body, that occur in progressive wavelike contractions. Peristaltic waves occur in the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. The waves can be short, local reflexes or long, continuous contractions that travel the whole length of the organ.
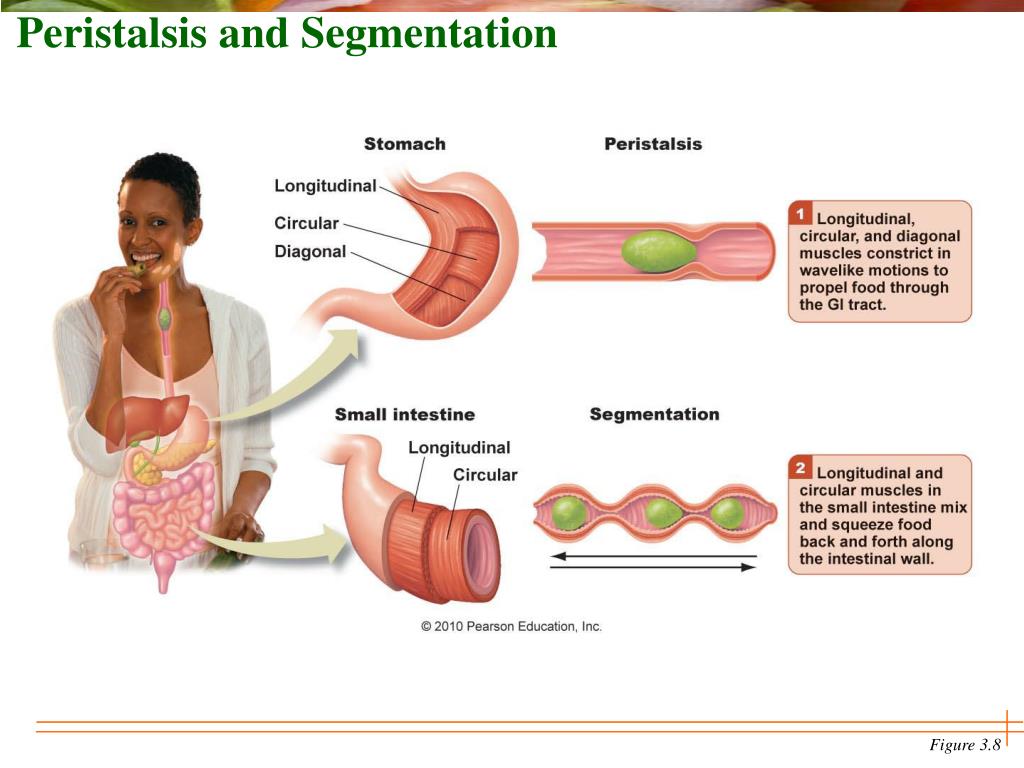
PPT Chapter 3 Digestion, Absorption, and Transport PowerPoint Presentation ID6011744
Peristalsis is a smooth muscle contraction movement that occurs throughout the GI tract and functions to propel the food through the GI tract in one direction only.In contrast, Segmentation is another involuntary smooth muscle contraction that occurs only in the intestine. In segmentation, the contraction occurs back and forth and it functions not only to move the food but also to mix up and.
PPT Digestive System PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6128614
Peristalsis ( / ˌpɛrɪˈstælsɪs / PERR-ih-STAL-siss, US also /- ˈstɔːl -/ -STAWL-) [1] is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde direction.
Peristalsis function, where peristalsis occurs & peristalsis in the digestive tract
Peristalsis and segmentation are two contractions that occur in the body and are recognized as such. They are both examples of movement, but the former is only responsible for movement in one direction, whilst the latter is responsible for movement in both directions. Peristalsis Vs. Segmentation